Robotic Surgery
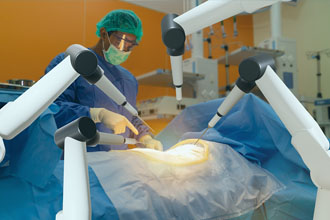 Different types of computer-assisted surgical systems can be used for pre-operative planning, surgical navigation and to assist in performing surgical procedures. Robotically-assisted surgical (RAS) devices are one type of computer-assisted surgical system. Sometimes referred to as robotic surgery, RAS devices enable the surgeon to use computer and software technology to control and move surgical instruments through one or more tiny incisions in the patient’s body (minimally invasive) for a variety of surgical procedures.
Different types of computer-assisted surgical systems can be used for pre-operative planning, surgical navigation and to assist in performing surgical procedures. Robotically-assisted surgical (RAS) devices are one type of computer-assisted surgical system. Sometimes referred to as robotic surgery, RAS devices enable the surgeon to use computer and software technology to control and move surgical instruments through one or more tiny incisions in the patient’s body (minimally invasive) for a variety of surgical procedures.
The benefits of a RAS device may include its ability to facilitate minimally invasive surgery and assist with complex tasks in confined areas of the body. Most surgeons use multiple surgical instruments and accessories with the RAS device, such as scalpels, forceps, graspers, dissectors, cautery, scissors, retractors and suction irrigators.
The FDA has cleared RAS devices for use by trained physicians in an operating room environment for laparoscopic surgical procedures in general surgery cardiac, colorectal, gynecologic, head and neck, thoracic and urologic surgical procedures. Some common procedures that may involve RAS devices are gall-bladder removal, hysterectomy and prostatectomy (removal of the prostate).
